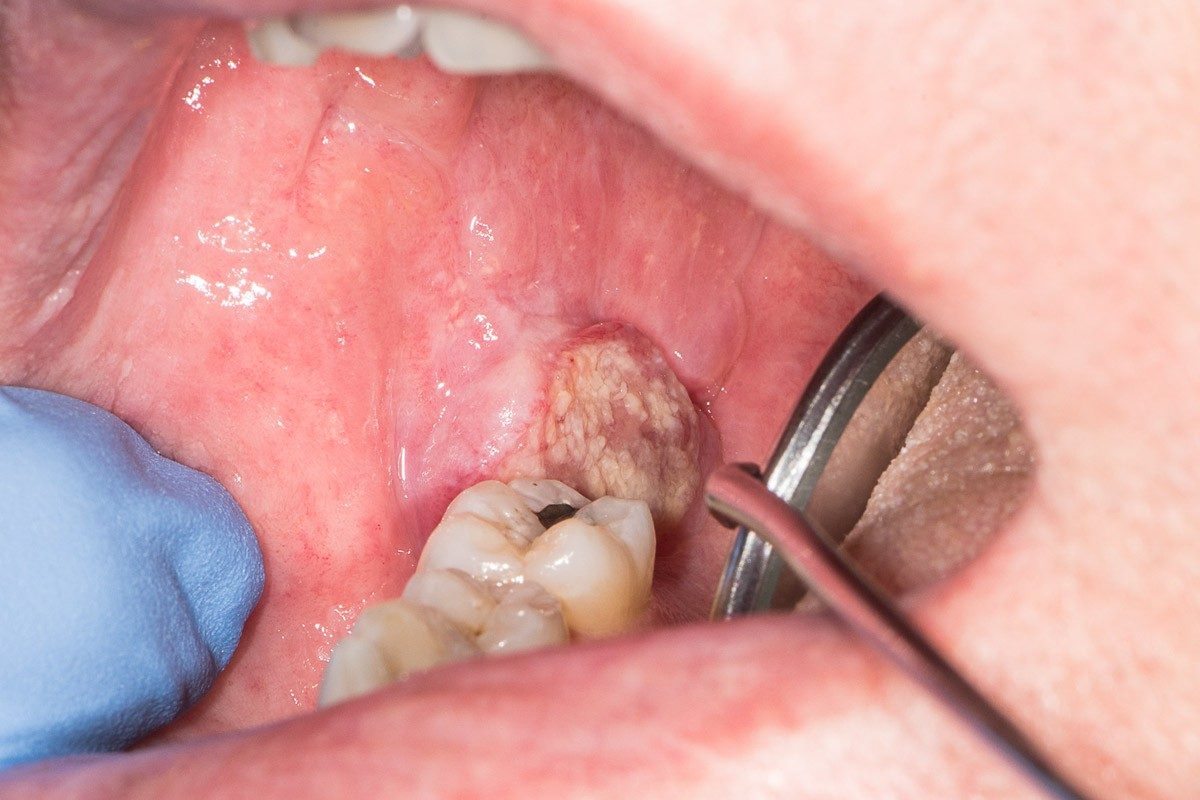
Accurate diagnosis is crucial in the fight against oral cancer, and imaging tests play a vital role in this process. As a Fairhope dentist, recognizing the importance of early detection and diagnosis is key to providing optimal care for patients. Imaging tests such as X-rays, CT scans, MRI scans, and PET scans help dentists and oral surgeons visualize the extent of the disease, identify potential tumors, and develop effective treatment plans. By leveraging these advanced imaging technologies, dental professionals can improve patient outcomes and save lives.
In this article, we will discuss the different types of imaging tests used in oral cancer diagnosis and their significance in the diagnostic process.
Types of Imaging Tests Used in Oral Cancer Diagnosis
Several imaging tests are used to diagnose and stage oral cancer. These include:
- X-rays: X-rays are the most commonly used imaging test for oral cancer diagnosis. They provide a two-dimensional image of the teeth, jawbone, and surrounding tissues.
- Computed Tomography (CT) Scans: CT scans use X-rays and computer technology to produce detailed cross-sectional images of the head and neck. They help identify the size and location of the tumor.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Scans: MRI scans use magnetic fields and radio waves to produce detailed images of the soft tissues in the head and neck. They help identify the extent of the tumor and its relationship to surrounding tissues.
- Positron Emission Tomography (PET) Scans: PET scans use small amounts of radioactive material to produce images of the body’s metabolic activity. They help identify the presence of cancer cells and monitor treatment response.
- Ultrasound: Ultrasound uses high-frequency sound waves to produce images of the soft tissues in the head and neck. It helps identify the size and location of the tumor.
| Oral cancer, also known as mouth cancer, is a type of cancer that occurs in the oral cavity, which includes the lips, tongue, gums, lining of the cheeks, and the floor and roof of the mouth. It is a malignant growth that develops in the cells of the mouth, often as a result of genetic mutations caused by environmental factors such as tobacco use, excessive alcohol consumption, and human papillomavirus (HPV) infection. |
The Role of Imaging Tests in Oral Cancer Diagnosis
Imaging tests play a crucial role in the diagnosis and staging of oral cancer. They help:
- Identify the presence of cancer: Imaging tests help identify the presence of cancer cells in the mouth, lips, tongue, or throat.
- Determine the size and location of the tumor: Imaging tests help determine the size and location of the tumor, which is essential for treatment planning.
- Assess the extent of the tumor: Imaging tests help assess the extent of the tumor and its relationship to surrounding tissues.
- Monitor treatment response: Imaging tests help monitor treatment response and identify any changes in the tumor.
- Detecting recurrence: Imaging tests help detect recurrence of oral cancer.
Advantages of Imaging Tests in Oral Cancer Diagnosis
Imaging tests offer several advantages in oral cancer diagnosis, including:
- Non-invasive: Imaging tests are non-invasive, which means they do not require surgery or insertion of instruments into the body.
- Painless: Imaging tests are painless, which makes them a comfortable option for patients.
- Quick results: Imaging tests provide quick results, which enables healthcare providers to make timely treatment decisions.
- High accuracy: Imaging tests have high accuracy, which ensures that healthcare providers can rely on the results to make informed treatment decisions.
Bottom Line
Imaging tests play a vital role in the diagnosis and staging of oral cancer. They help identify the presence of cancer cells, determine the size and location of the tumor, assess the extent of the tumor, monitor treatment response, and detect recurrence. Healthcare providers must carefully interpret the results of imaging tests and use them in conjunction with other diagnostic tools to ensure accurate diagnosis and effective treatment.